Create a Bluetooth Low Energy repeater using Raspberry pi
April 1, 2021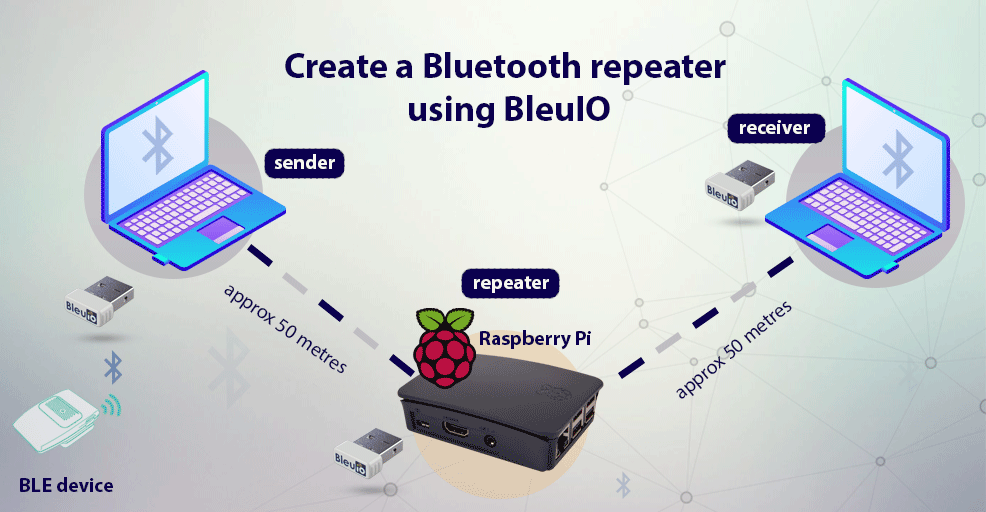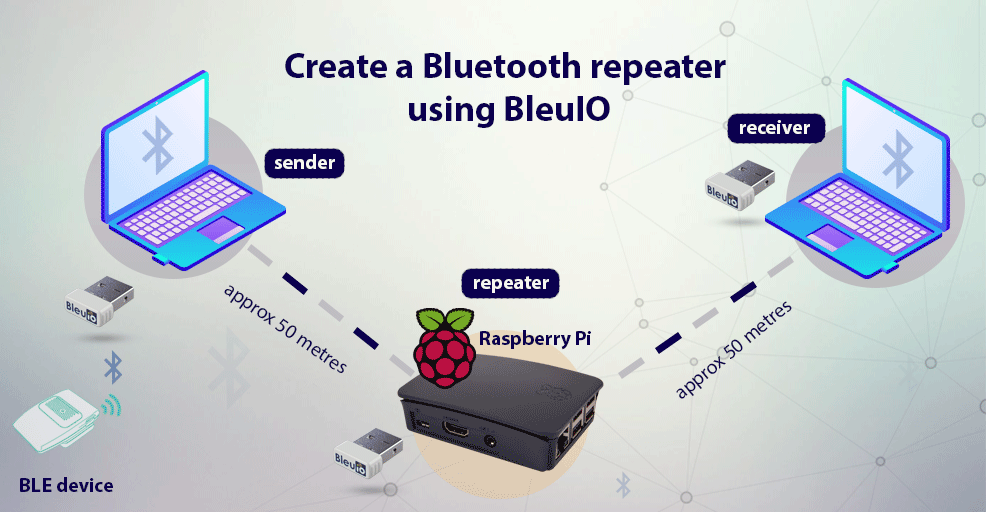
Bluetooth low energy technology offers a suitable way of connecting smart devices.
However, despite the convenience, you can bear witness that the range offered can be a little limiting. Sometimes the connection tends to drop or lag when you move a little further away from the device. Fortunately, it’s easy to overcome this range limitation with the Bluetooth repeater.
This article will explain how to create a BLE Repeater using BLE USB dongle called BleuIO and python.
The BleuIO is Bluetooth low energy solution that can be used to create new BLE 5.0 applications in the fastest and easiest way. Using this dongle’s multi-connection feature, we will make a simple repeater where one dongle scans nearby devices data and sends it to the repeater. At the same time, the repeater passes the data to the receiver dongle. And that’s how a repeater will help us overcome the range limitation.
For this project, sender dongle will scan for air quality data from HibouAir device and pass the advertised data along with timestamp to the repeater. The repeater dongle will be connected to a Raspberry pi which will forward data to the receiver dongle.
We have already created a sample script in python, which will help us to do the task.
Requirements :
- 3 pcs BleuIO Dongle.
- HibouAir or any BLE device
- Python 2.7 or Python 3.4 and newer
- pyserial 3.5
Task:
Step 1:
Let’s start by cloning the repository from https://github.com/smart-sensor-devices-ab/bleuio_repeater_example
Once you cloned the script, you will find three different python script called
- repeater_example_reciever_dongle.py
- repeater_example_repeter_dongle.py
- repeater_example_sender_dongle.py

We need to update the ports on those scripts manually.
repeater_example_reciever_dongle.py
import time
from bleuio_lib.bleuio_funcs import BleuIo
reciever_dongle_port = "COM74" # Change this to your dongle's COM port
mac_addr_to_repeater = (
"[0]40:48:FD:E5:2D:74" # Change this to your repeater dongle's mac address
)
buffer = ""
connected = False
connecting = ""
reciever_dongle = BleuIo(port=reciever_dongle_port)
reciever_dongle.start_daemon()
print("Dongle found.")
def save_msg(buffer):
"""
Parses incomming data string for just the data and prints it out.
"""
result = buffer
result_array1 = result.split("\r\n")
result_array = result_array1[2].split(" ")
msg_to_save = str(result_array[0])
print("Recieved = " + msg_to_save)
try:
reciever_dongle.at_dual()
ready = input(
"Press enter to connect to the repeater dongle. (This should be connected first)."
)
print("Connecting...")
reciever_dongle.at_gapconnect(mac_addr_to_repeater)
time.sleep(5)
while not connected:
connected_status = reciever_dongle.ati()
if "\r\nConnected" in connected_status[0]:
connected = True
break
if "\r\nNot Connected" in connected_status[0]:
reciever_dongle.at_gapconnect(mac_addr_to_repeater)
time.sleep(5)
print("Trying to connect...")
time.sleep(2)
print("Connected.")
print("Waiting to recieve...")
while 1:
buffer = reciever_dongle.rx_buffer.decode("utf-8", "ignore")
if "\r\nhandle_evt_gattc_notification:" in buffer:
save_msg(buffer)
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
reciever_dongle.at_cancel_connect()
reciever_dongle.at_gapdisconnect()
reciever_dongle.at_advstop()
print("Shutting down script.")repeater_example_repeter_dongle.py
import time
from bleuio_lib.bleuio_funcs import BleuIo
repeter_dongle_port = "COM38" # Change this to your dongle's COM port
repeter_dongle = BleuIo(port=repeter_dongle_port)
repeter_dongle.start_daemon()
buffer = ""
num_of_connected_devices = 0
connection_list = []
print("Dongle found.")
repeter_dongle.at_dual()
repeter_dongle.at_advstart()
repeter_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
print("Waiting for other dongles to connect...")
def send_msg(buffer):
"""
Parses incomming data string for just the data and sends it forward via the Serial Port Service.
"""
try:
result = buffer
msg_to_send = ""
result_array1 = result.split("\r\n")
for line in result_array1:
if "[Received]:" in line:
msg_to_send = line.split(" ")
msg_to_send = msg_to_send[1]
break
print("Forwarding data to reciever:")
print(msg_to_send)
if not msg_to_send == "":
repeter_dongle.at_spssend(msg_to_send)
repeter_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
except:
print(" ")
try:
while 1:
buffer = repeter_dongle.rx_buffer.decode("utf-8", "ignore")
if "\r\nCONNECTED." in buffer:
num_of_connected_devices = num_of_connected_devices + 1
print("A Dongle has connected!")
repeter_dongle.at_advstart()
repeter_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
if "DISCONNECTED." in buffer:
num_of_connected_devices = num_of_connected_devices - 1
connection_list = []
print("No Dongles connected.")
if num_of_connected_devices > 1:
if "\r\n[Received]:" in buffer:
# print(buffer)
send_msg(buffer)
buffer = ""
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
repeter_dongle.at_advstop()
repeter_dongle.at_gapdisconnect()
print("Shutting down script.")repeater_example_sender_dongle.py
import time
from bleuio_lib.bleuio_funcs import BleuIo
import random
sender_dongle_port = "COM73" # Change this to your dongle's COM port
mac_addr_to_repeater = (
"[0]40:48:FD:E5:2D:74" # Change this to your repeater dongle's mac address
)
sender_dongle = BleuIo(port=sender_dongle_port)
sender_dongle.start_daemon()
connected = False
data = ""
buffer = ""
def scan_and_get_results():
"""
Starts a BLE scan for three seconds, looking for results including the 'FF' flag in the advertising data.
Then it saves the results in a list and returns one of the results as a string.
:return: string
"""
print("Scanning...")
return_data = ""
result_list = []
time.sleep(0.5)
try:
scanning = sender_dongle.at_findscandata("FF")
if "SCANNING" in scanning[0]:
time.sleep(4)
sender_dongle.stop_scan()
time.sleep(0.5)
result_list = sender_dongle.rx_scanning_results
if not result_list == []:
if len(result_list) > 3:
lines = result_list[2].split("\r\n")
if not lines[1] == "":
data_array = lines[1].split(" ")
lenght = len(data_array)
if lenght == 5:
data = data_array[4]
return_data = data
else:
sender_dongle.stop_scan()
result_list = []
sender_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
return_data = ""
except:
sender_dongle.stop_scan()
result_list = []
sender_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
return_data = ""
return return_data
print("Dongle found.")
try:
sender_dongle.at_dual()
ready = input(
"Press enter to connect to the repeater dongle. (This should be connected last)."
)
print("Connecting...")
sender_dongle.at_gapconnect(mac_addr_to_repeater)
time.sleep(5)
while not connected:
connected_status = sender_dongle.ati()
if "\r\nConnected" in connected_status[0]:
connected = True
break
if "\r\nNot Connected" in connected_status[0]:
sender_dongle.at_gapconnect(mac_addr_to_repeater)
time.sleep(5)
print("Trying to connect...")
time.sleep(2)
print("Connected.")
print("Getting services...")
get_services = sender_dongle.at_get_services()
sender_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
time.sleep(2)
ready = input("Press enter to start sending data to the repeater dongle.")
while 1:
data = scan_and_get_results()
time.sleep(1)
if not data == "":
sent = sender_dongle.at_spssend(data)
time.sleep(0.1)
if len(sent) == 1:
if "[Sent]" in sent[0]:
print("Data = (" + data + ") sent.")
time.sleep(1)
data = ""
time.sleep(1)
sender_dongle.rx_state = "rx_waiting"
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sender_dongle.at_gapdisconnect()
print("Shutting down script.")Step 2:
Connect two dongles on your PC. You can do the process on three different PC or Raspberry Pi.
For this project, I have connected both the sender and receiver dongles to one PC.
After connecting the dongles, open device manager (windows) to find ports of each dongle.

On my PC, I have two dongles connected on port 5 and 6.
Let’s make COM 5 as the sender, COM 6 as a receiver.
Now open the scripts and set the ports number accordingly.
We also need to know repeater dongles ID. To do that, we can simply advertise the dongle on Raspberry pi using AT+ADVSTART command .Then do a gapscan using AT+GAPSCAN from sender dongle and look for a dongle called BleuIO

Once we have repeater dongles id, we can put it on our scripts.
Step 3 :
Now lets run the script.
First move to the script directory on Raspberry pi and using command prompt type sudo python3 repeater_example_repeter_dongle.py to run repeater script.
Similarly, run receiver and sender scripts accordingly on PC.
As the name suggests, the repeater will repeat its content. On the terminal, we will see the message sent to the repeater from the sender, and the repeater forwards the data to the receiver dongle.

Follow this video for a better understanding.

